paper collection
[Similarity KD 2019] Similarity-Preserving Knowledge Distillation
[CWD 2020] Channel-wise Knowledge Distillation for Dense Prediction
Similarity-Preserving Knowledge Distillation
与其他KD methods的区别:
- the student is not required to mimic the representation space of the teacher, but rather to preserve the pairwise similarities in its own representation space
- 监督student和teacher的similarity
- 适用场景:
- feature shape对不齐:channel/stride,也可以用1x1 conv对齐
- CNN/transformer之间的KD,模型本质diversity就不同
method
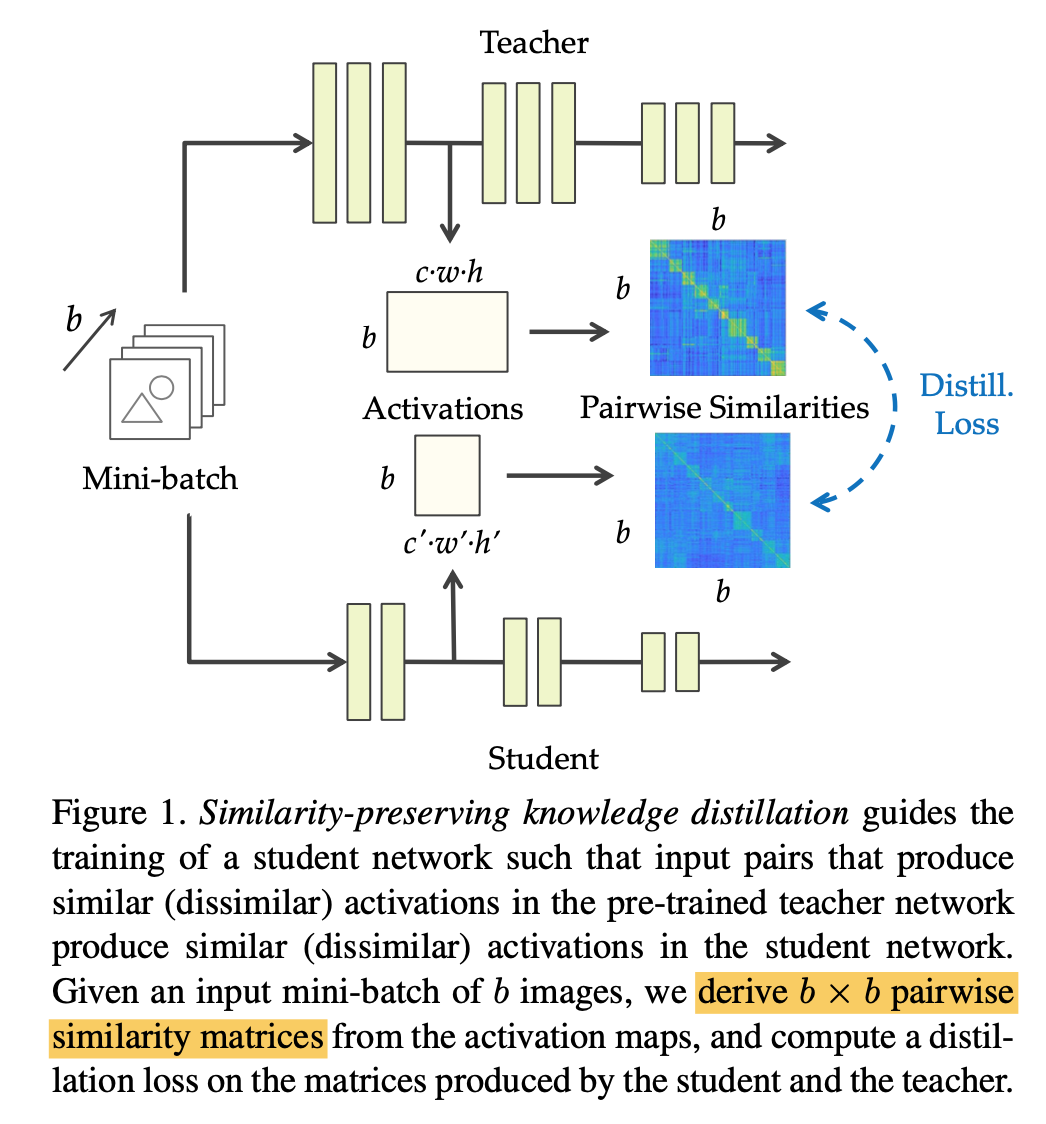
given activation map(feature)$F$
- compute similarity:$F*F^T/L2norm(F)$
- compute KD loss:$\frac{1}{b^2}MSE(t,s)$
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def similarity_loss(self, f_s, f_t):
bs = f_s.shape[0]
f_s = f_s.view(bs, -1)
f_t = f_t.view(bs, -1)
G_s = f_s * f_s.T # bxb
G_s = F.normalize(G_s, p=2, dim=1)
G_t = f_t * f_t.T
G_t = F.normalize(G_t, p=2, dim=1)
G_diff = G_t - G_s
loss = (G_diff * G_diff).view(-1).sum() / (bs * bs)
return loss
其他KD methods
response based:KL divergence loss
作用于softmax以后的probs(可以有temperature factor)
$L_{RD} (p_t, p_s) = L_R (p_t, p_s)$
$L_R()$通常是KL divergence loss
KL divergence loss
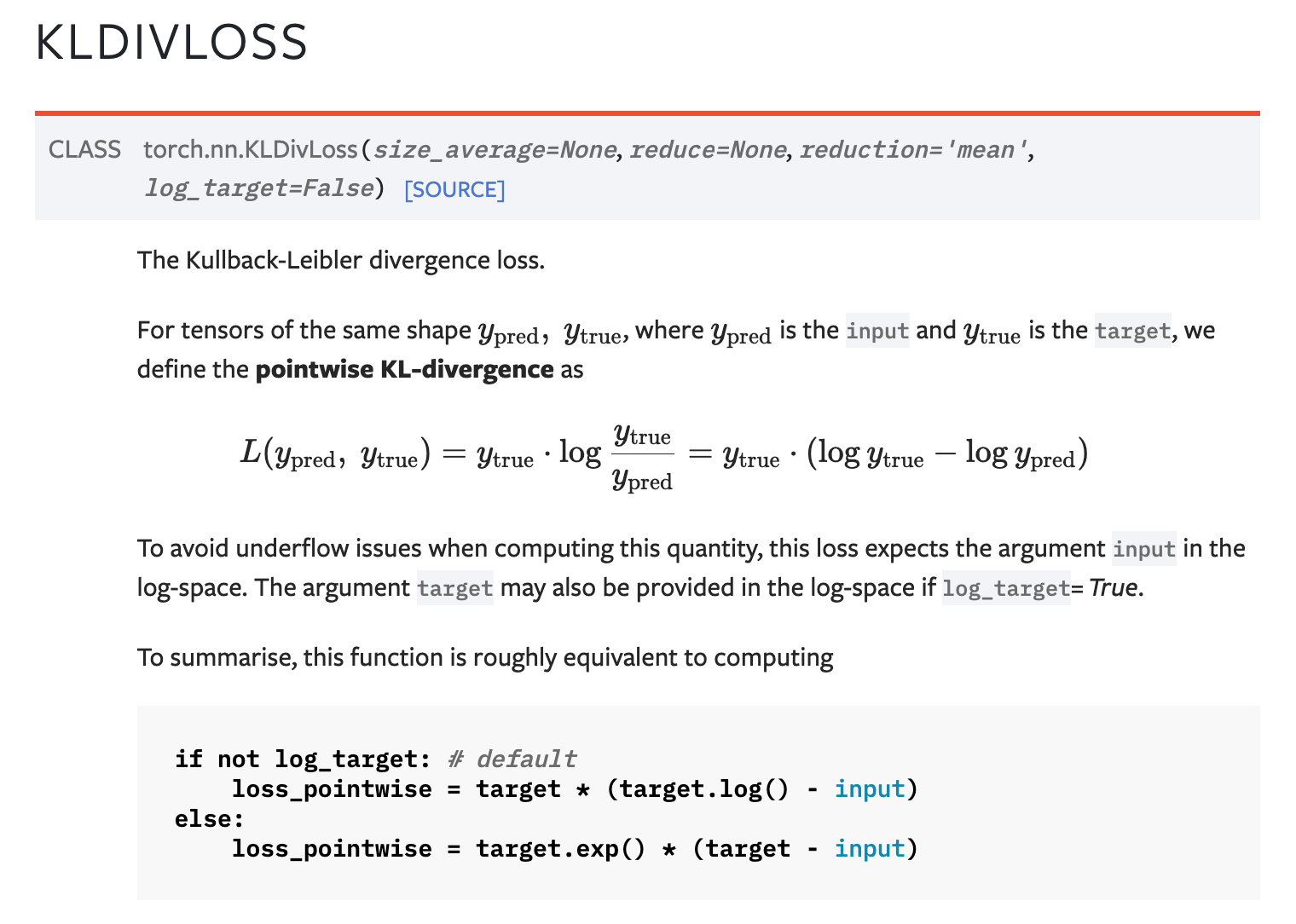
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12# pred在调用KLDivLoss方法计算loss时先做log,防止先两个normed prob先做除法损失精度
pred = F.log_softmax(torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True))
target = F.softmax(torch.rand(3, 5))
loss = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction="batchmean")(pred, target)
# target在调用KLDivLoss时也可以先做log
log_target = F.log_softmax(torch.rand(3, 5))
output = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction="batchmean", log_target=True)(pred, log_target)
def kl_categorical(p_logit, q_logit):
p = F.softmax(p_logit, dim=-1)
_kl = torch.sum(p * (F.log_softmax(p_logit, dim=-1) - F.log_softmax(q_logit, dim=-1)), -1)
return torch.mean(_kl)
feature based
- $L_{FD} (f_t, f_s) = L_F (\Phi_s(f_t), \Phi_s(f_s))$
- $\Phi()$是transform function,用来align feature dimension
- $L_F()$是similarity function,通常可以是L1、L2、L_CE、L_MMD
- MMD:maximum mean discrepancy