papers
[2021 CLIP] Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision
[2022 MaskCLIP] Extract Free Dense Labels from CLIP
[2022 DenseCLIP ]DenseCLIP: Language-Guided Dense Prediction with Context-Aware Prompting
CLIP: Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision
动机
- visual tasks通常建模成给定的图预测成给定类别的任务,大大限制了数据的可用量
- this paper
- leverage language concepts
- build a simple pretraining task:predicting which caption goes with which image
- use 400 million image-text pairs from internet
- train from scratch
- enable zero-shot transfer to downstream tasks
overview
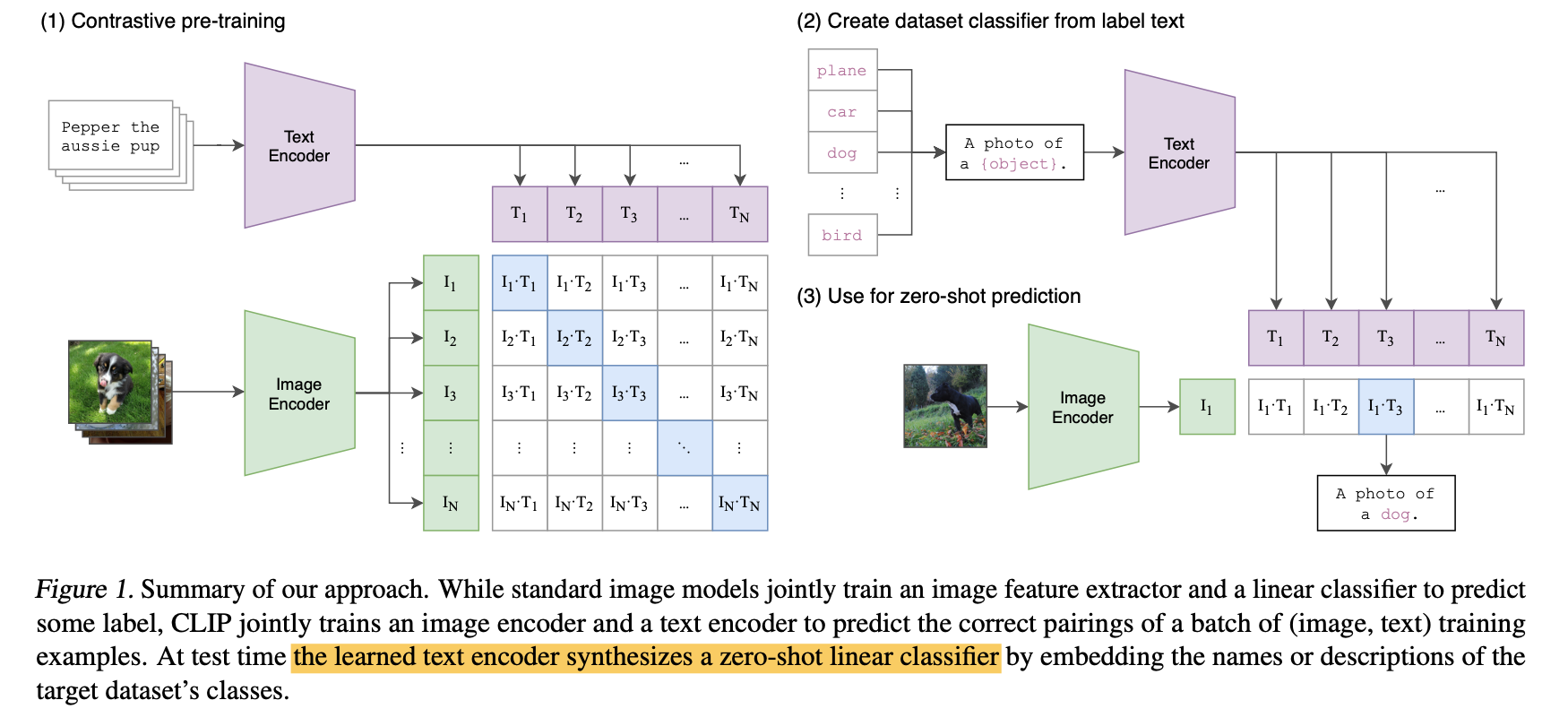
- 图1是pretraining模型
- 图2是获取给定text set,构建prompt,然后encoder得到固定的linear classifier
- 图3是zero-shot classification,就是给每个样本的image embedding,用上述linear classifier做logistics regression,得到其匹配不同类别的概率
方法
Creating a Sufficiently Large Dataset
- construct a new dataset of 400 million image-text pairs from a variety of publicly available sources on the Internet
- base query:Wikipedia里面出现100次以上的单词,a set of 500,000
- search policy:基于base query的单词表搜索,balancing by 20,000 paris per query
Selecting an Efficient Pre-Training Method
第一次尝试:
- jointly train a image CNN & a text transformer
- 发现transformer模型对有限的1000类都收敛极慢,对开放词典及其不友好
然后建立了a easier task
- 只需要预测哪个text和哪个image匹配,而不用预测the exact text
- 4x efficiency in zero-shot transfer
formulation
- given a batch of N (image, text) pairs
- jointly train an image encoder & a text encoder,将其映射到multi-modal embedding space
- predict NxN pairings
- 最大化pairs的cosine similarity,最小化$N^2-N$的incorrect pairings
optimize a symmetric cross entropy loss

Choosing and Scaling a Model
- two different structures for Image CNN
- ResNet & ViT
- ResNet的gloval average pooling改成了transformer-stype的attention pooling
- 用global query作为feature representation
- text encoder
- 就是一个现成的transformer
- token向量operates on a lower-cased byte pair encoding (BPE)
- sentence最长76,add SOS & EOS
- EOS token作为feature representation,LN & linear projected into embedding space
- two different structures for Image CNN
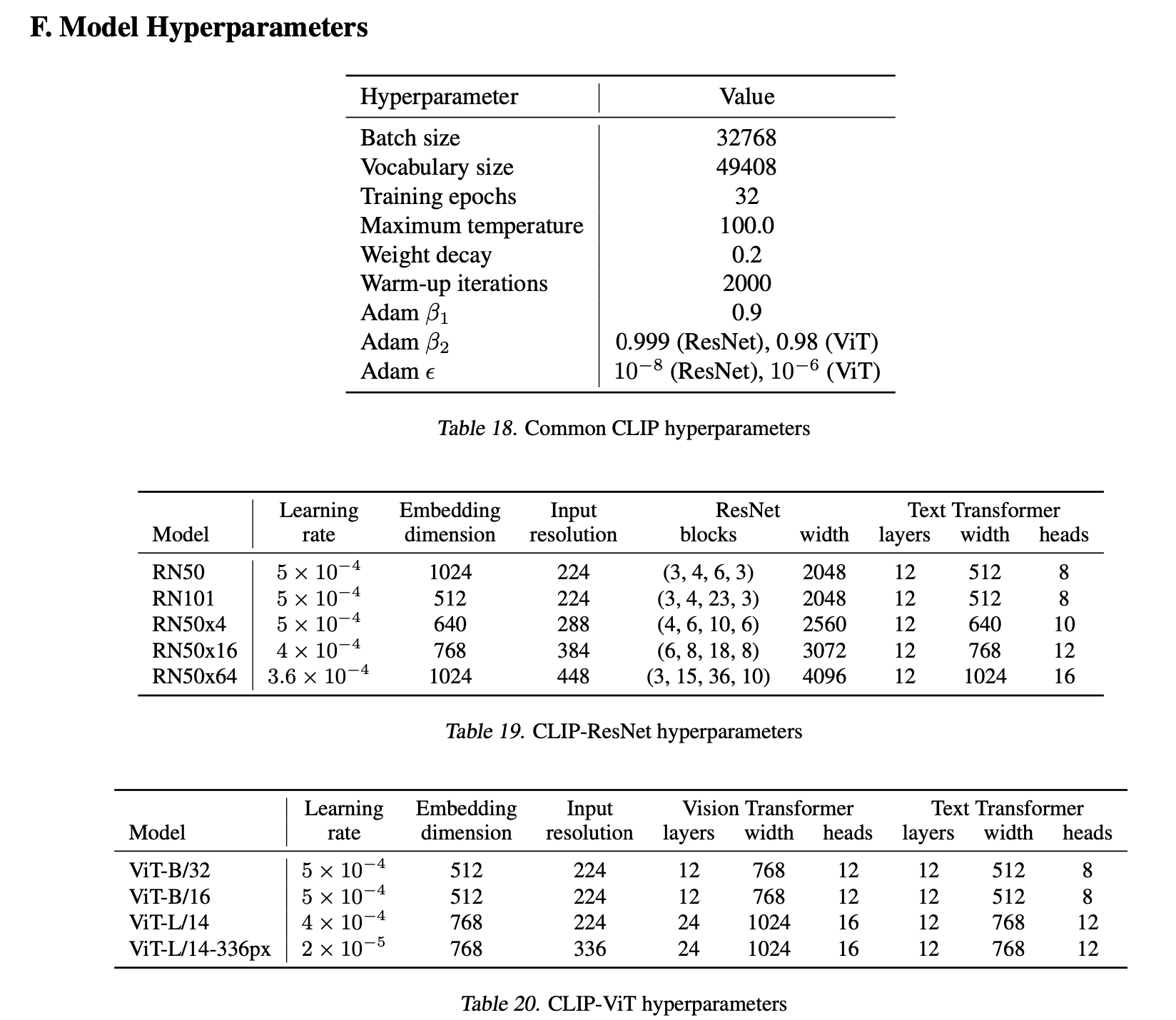
Model Zoo
- 5 ResNets
- ResNet-50, ResNet-101
- RN50x4, RN50x16, and RN50x64:4x, 16x, and 64x computation models follow EfficientNet-style model scaling
- 3 ViTs
- ViT-B/32, a ViT-B/16, and a ViT-L/14
- ViT-L/14@336px:在224基础上,用336的resolution train one additional epoch
temperature parameter
- 0.07,clip to prevent scaling the logits by more than 100
- 原始的logits/T,但是新logits不超过100
- 这是因为cosine similarity的输出在[-1,1],而一般用于分类预测的logits通常是不限幅的,所以用temperature factor来拉大cos logits之间的差异,提高正样本置信度
- necessary for training stability
- 5 ResNets
实验
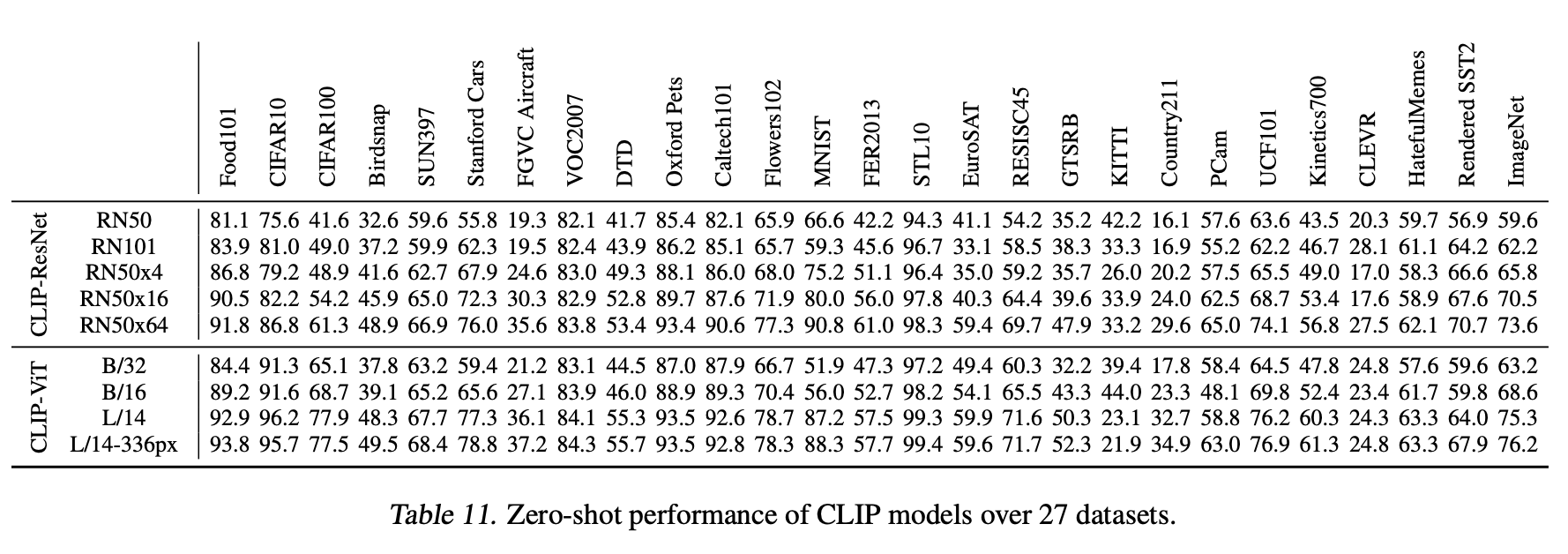
Zero-Shot Transfer
- 实验发现CLIP对unseen datasets(没有用于训练当前模型的数据集)有很好的zero-shot transfer能力,主要是因为它在互联网上见的太多了
- zero-shot classification pipeline:详见overview的图
- 用目标数据集,所有类别,作为text pairings set,然后预测样本的most probable image-text pair
- 首先获得各自的feature embedding,各自L2-norm
- 然后计算cosine similarity,scaled by temperature factor
- 然后normalized by softmax into probability
精度
- leaderboard上ResNet101的精度:top1@80.98%,top5@95.51%
- leaderboard上ResNet50的精度:top1@79.25%,top5@94.65%
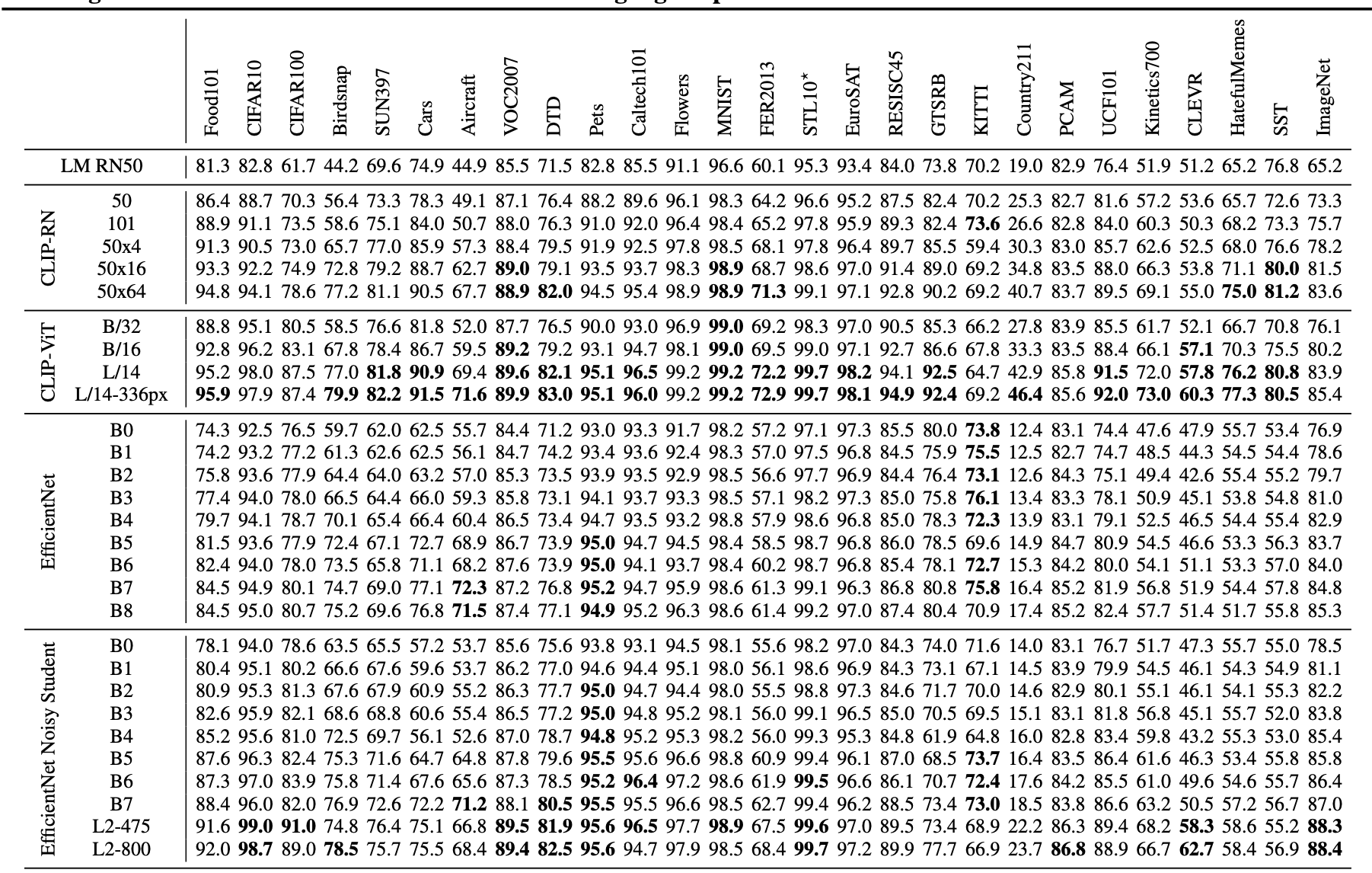
Representation Learning
linear-probe pipeline
- 固定住pretrained model
- fitting一个linear classifier
- 这样相比较于finetuning的好处是hyper比较少,同时特征比较general/class-agnostic
findings
- small models(RN50/RN101)在ImageNet-21K上打不过对应模型
- small models在同样数据集上也打不过efficientNet家族
- 但是大模型(RN50x64)能够打败目前最好的(Noisy Student EfficientNet-L2)
CLIP transformers are 3x more compute efficient than CLIP ResNets,能够在同样的算力条件下获得更好的performance
prompt engineering and ensembling
- 图像数据集的类别大多是id/一个单词
- prompt将其构造成一个句子:a photo of {word} / a {specific} of {word}
- ensemble将多种构造的embedding求mean