GPT papers,openAI三部曲,通用预训练模型
- [2018 GPT-1] Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training:transformer-based,pre-training+task-specific finetuning,将所有的task的输入都整合成sequence-to-sequence form,结构上不需要task-specific architecture
- [2019 GPT-2] Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners:对GPT-1结构上微调,引入huge dataset进行无监督训练
[2020 GPT-3] Language models are few-shot learners:scaling up LMs,zero-shot
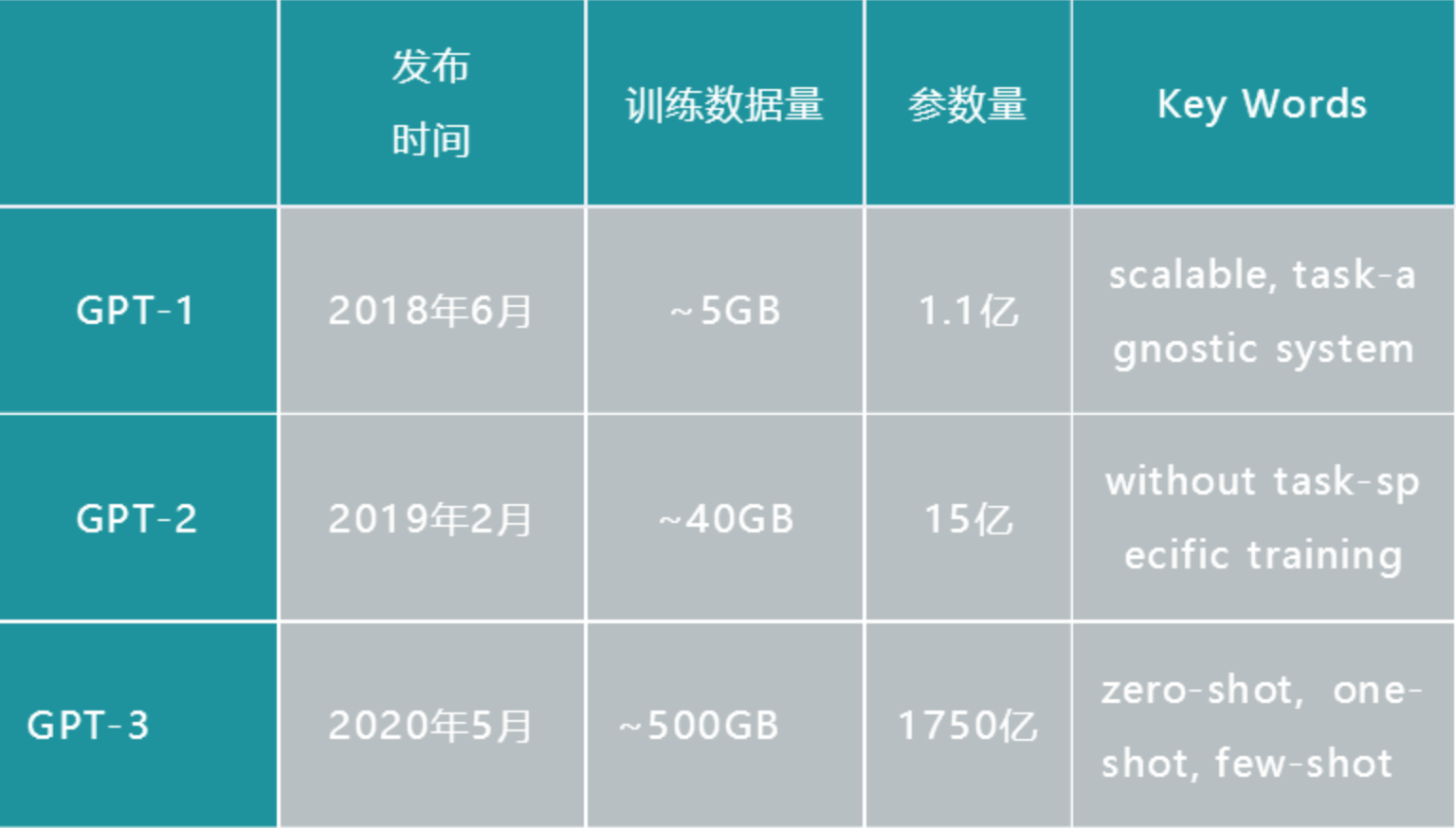
BERT有3亿参数
GPT-1: Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training
动机
- NLP tasks
- textual entailment:文本蕴含
- question answering
- semantic similarity assessment
- document classification
- labeled data少,unlabeled corpora充足
- large gains can be realized by
- generative pre-training of a language model on diverse unlabeled corpus,无监督general model,learn universal representations
- discriminative fine-tuning on specific task,有监督task-specific model,adapt to wide range of tasks
- general task-agnostic model能够打败discriminatively trained models
- use task-aware input transformations
- NLP tasks
论点
- learn from raw text &alleviate the dependence on supervised learning still challenging:
- 不清楚选什么optmization objectives:language modeling/machine translation/discourse coherence
- effective way to transfer:加task-specific模型结构改动/auxiliary learning objectives/learning schemes
- two-stage training procedure
- pretrain + fine-tuning
- use Transformer:better handling long-term dependencies
- task-specific input adaptions将输入处理成structured词向量序列
- evaluate on
- natural language inference
- question answering
- semantic similarity
- text classification
- learn from raw text &alleviate the dependence on supervised learning still challenging:
方法
overview
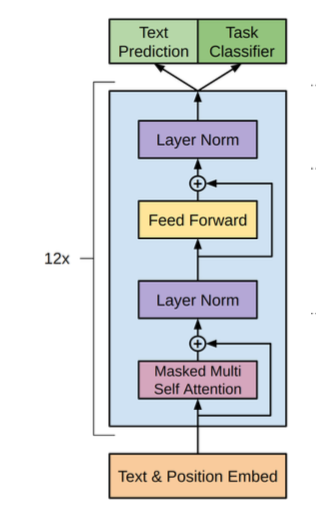
- architecture:transformer decoder
- training objectives
- unsupervised:text prediction,前文预测后文
- supervised:task classifier,对整个序列分类
Unsupervised pre-training
- given unsupervised corpus of tokens $U={u_1, …, u_n}$
- context window size $k$
- use standard language modeling objective:$L_1(U)=\sum log P(u_i|u_{i-k},…,u_{i-1};\Theta)$
- use multi-layer Transformer decoder
- input:$h_0 = UW_e + W_p$
- attention blocks:$h_l = tranformer_block(h_{l-1}), \forall l\in[1,n]$
- output:$P(u)=softmax(h_l W_e^T)$
- use SGD
Supervised fine-tuning
given labeled dataset $C$ consists of $[x^1,…,x^m;y]$ instances
use the final transformer block’s activation $h_l^m$
fed into an linear+softmax output layer:$P(y|x^1,…,x^m)=softmax(h_l^mW_y)$
优化目标是y:$L_2(C) = \sum log(P(y|x^1,…,x^m))$
实验发现加上Unsupervised loss helps learning:提升泛化性,加速收敛
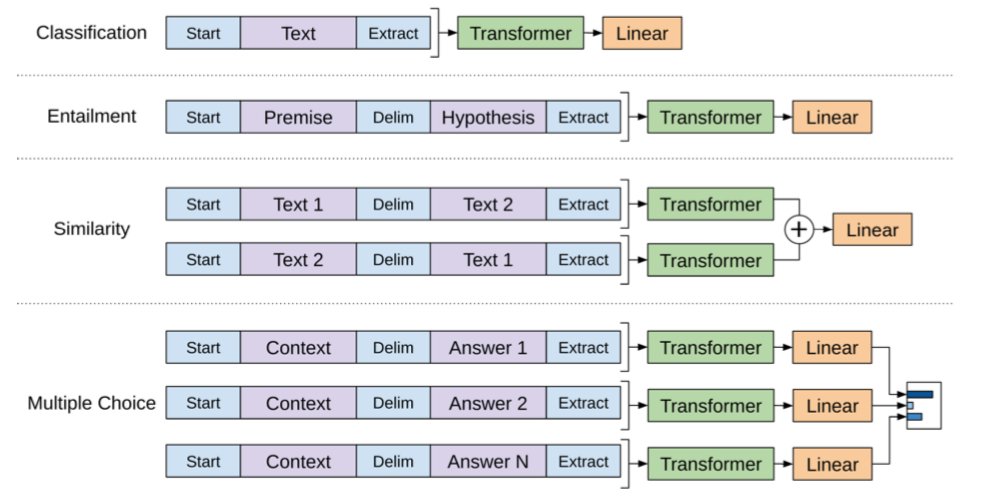
Task-specific input transformations
- certain tasks has structured inputs如问答pairs/triplets
- we convert them into ordered sequences
- Textual entailment:将前提premise和推理hypothesis concat在一起
- Similarity tasks:两个文本没有先后顺序关系,所以一对文本变成顺序交换的两个sequence,最后的hidden units $h^m_l$相加,然后接输出层
- Question Answering and Commonsense Reasoning:given document $z$, question $q$, and possible answers $\{a_k\}$,context $zq$和每个答案$a_i$都构造一组连接,然后分别independently processed with our model,最后共同接入一个softmax,生成对所有possible answers的概率分布
- 所有的连接都使用分隔符$
所有的sequence的首尾都加上一个randomly initialized start&end tokens
实验
GPT-2: Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners
动机
- more general models which can perform many tasks
- train language model
- without explicit supervision
- trained on a new dataset of millions of webpages called WebText
- outperforms several baselines
- GPT-2:a 1.5B parameter Transformer
论点
- Machine learning systems are sensitive to slight changes of
- data distribution
- task specification
- ‘narrow experts’
- lack of generalization since ingle task training on single domain datasets
- methods
- multitask training:还不成熟
- pretraining + finetuning:still require supervised training
- this paper
- connect the two lines above
- perform donw-stream tasks in a zero-shot setting
- Machine learning systems are sensitive to slight changes of
方法
natural sequential characteristic makes the general formulation $p(output|input)$
task specific system requires the probabilistic framework also condition on the task to be performed $p(output|input, task)$
- architectural level:task-specific encoders/decoders
- algorithmic level:like MAML
- or in a more flexible way to specify tasks:write all as sequences
- translation:(translate to french, english text, french text)
- comprehension:(answer the question, document, question, answer)
training dataset
- 海量document可以通过爬虫获得but significant data quality issues
- 与target dataset similar的外部doc的子集能够给到提升
- 因此本文设定了一个搜集文本的机制:Reddit的外链,去掉Wikipedia
input representation
word-level language model VS byte-level language model
- word-level performs better
- 但是受到vocabulary限制
Byte Pair Encoding (BPE)
combine the empirical benefits of word-level LMs with the generality of byte-level approaches
具体改进还没理解
model
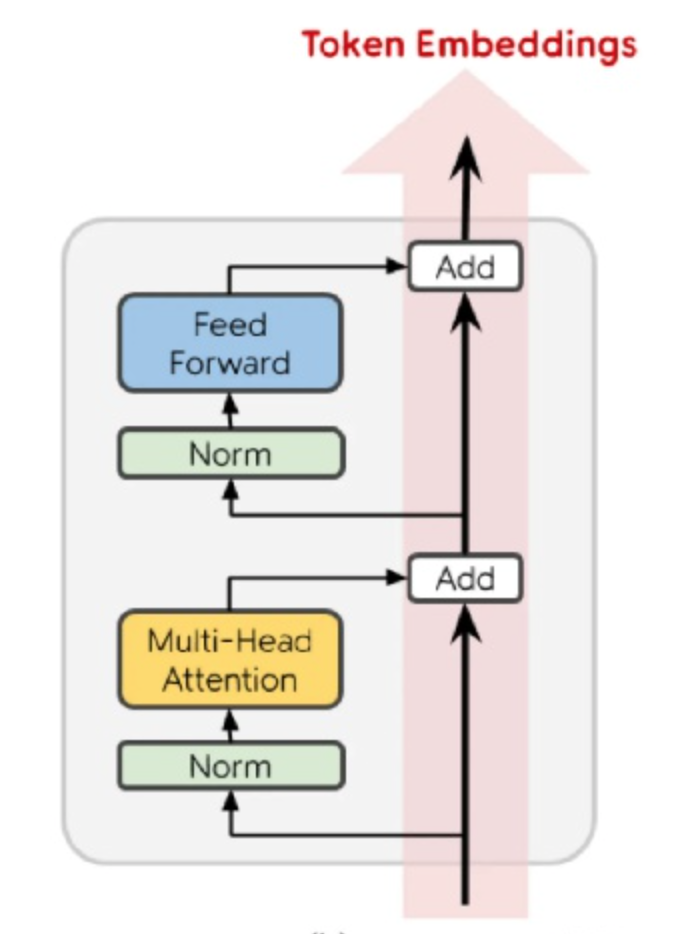
Transformer-based,few modifications on GPT-1 model
- layer normalization was moved to the input of each sub-block
- additional layer normalization was added after the final self-attention block
- initialization on residual path:N个residual layers,就将residual weights rescale $\frac{1}{\sqrt{N}}$
- context size:1024
- batch size:512
residual block
实验
GPT-3: Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
- 动机
- zero-shot:pretraining+finetuning scheme还是需要task-specific finetuning datset
- scale-up:scaling up language models greatly improves general few-shot performance