reference:
https://blog.janestreet.com/l2-regularization-and-batch-norm/
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/56142484
https://vitalab.github.io/article/2020/01/24/L2-reg-vs-BN.html
解释了之前的一个疑点:
- 在keras自定义的BN层中,没有类似kernel_regularizer这样的参数
- 在我们写自定义optmizer的时候,BN层也不进行weight decay的
L2 Regularization versus Batch and Weight Normalization
动机
- 两个common tricks:Normalization(BN、WN、LN等)和L2 Regularization
- 发现两者结合时L2 regularization对normalization层没有正则效果
- L2 regularization反而对norm layer的scale有影响,间接影响了learning rate
- 现代优化器如Adam只能间接消除这种影响
- 两个common tricks:Normalization(BN、WN、LN等)和L2 Regularization
论点
BN
- popular in training deep networks
- solve the problem of covariate shift
- 使得每个神经元的输入保持normal分布,加速训练
- mean & variance:training time基于每个mini-batch计算,test time使用所有iteration的mean & variance的EMA
usually trained with SGD with L2 regularization
result in weight decay:从数学表示上等价于对权重做衰减
每一步权重scaled by a 小于1的数
- 但是normalization strategies是对scale of the weights invariant的,因为在输入神经元之前都会进行norm
- therefore
- there is no regularizing effect
- rather strongly influence the learning rate??👂
L2 Regularization
formulation:
- 在loss的基础上加一个regularization term,$L_{\lambda}(w)=L(w)+\lambda ||w||^2_2$
- loss是每个样本经过一系列权重运算,$L(w)=\sum_N l_i (y(X_i;w,\gamma,\beta))$
- 当使用normalization layer的时候:$y(X_i;w,\alpha,\beta)=y(X_i;\alpha w,\gamma,\beta)$,即loss term不会变
- $L_{\lambda}(\alpha w)=L(w)+\lambda||w||^2_2$
- 在有normalization layer的时候,L2 penalty还是能够通过reg term force权重的scale越来越小,但是不会影响优化进程(不影响main objective value),因为loss term不变
Effect of the Scale of Weights on Learning Rate
- BN层的输出是scale invariant的,但是梯度不是,梯度是成反比被抑制的!
所以weights在变小,同时梯度在变大!
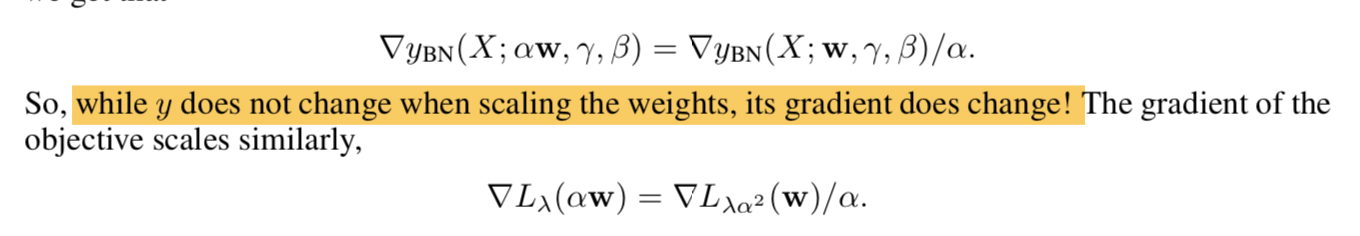
在减小weight scale的时候,网络的梯度会变大,等价于学习率在变大,会引起震荡不稳定
- 所以在设定hyper的时候,如果我们要适当加大weight decay $\lambda$,就要反比scale学习率
Effect of Regularization on the Scale of Weights
- during training the scale of weights will change
- the gradients of the loss function will cause the norm of the weights to grow
- the regularization term causes the weights to shrink
- during training the scale of weights will change