综述
正则
正则化是用来解决神经网络过拟合的问题,通过降低模型的复杂性和约束权值,迫使神经网络学习可泛化的特征
- 正则化可以定义为我们为了减少泛化误差而不是减少训练误差而对训练算法所做的任何改变
- 对权重进行约束
- 对目标函数添加额外项(间接约束权值):L1 & L2正则
- 数据增强
- 降低网络复杂度:dropout,stochastic depth
- early stopping
- 我们在对网络进行正则化时不考虑网络的bias:正则表达式只是权值的表达式,不包含bias
- bias比weight具有更少的参数量
- 对bias进行正则化可能引入太多的方差,引入大量的欠拟合
- 正则化可以定义为我们为了减少泛化误差而不是减少训练误差而对训练算法所做的任何改变
L1 & L2:
要惩罚的是神经网络中每个神经元的权重大小
L2关注的是权重的平方和,是要网络中的权重接近0但不等于0,“权重衰减”
L1关注的是权重的绝对值,权重可能被压缩成0,权重更新时每次减去的是一个常量
L1会趋向于产生少量的特征,而其他的特征都是0,而L2会选择更多的特征,这些特征都会接近于0
dropout
- 每个epoch训练的模型都是随机的
- 在test的时候相当于ensemble多个模型
权重共享
数据增强
隐式正则化:其出现的目的不是为了正则化,而正则化的效果是其副产品,包括early stopping,BN,随机梯度下降
dropout & drop connect([Reference][https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/108024434])
dropout:
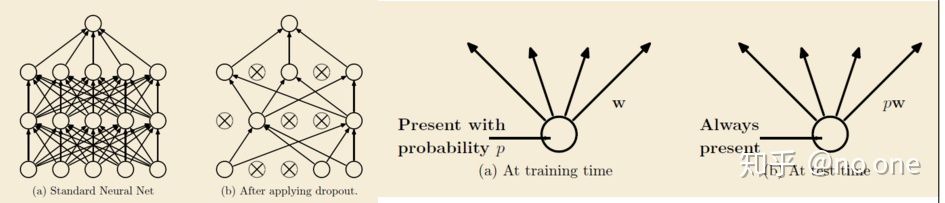
- 2012年Hinton提出,在模型训练时以概率p随机让隐层节点的输出变成0,暂时认为这些节点不是网络结构的一部分,但是会把它们的权重保留下来(不更新)。
标准dropout相当于在一层神经元之后再添加一个额外的层,这些神经元在训练期间以一定的概率将值设置为零,并在测试期间将它们乘以p。
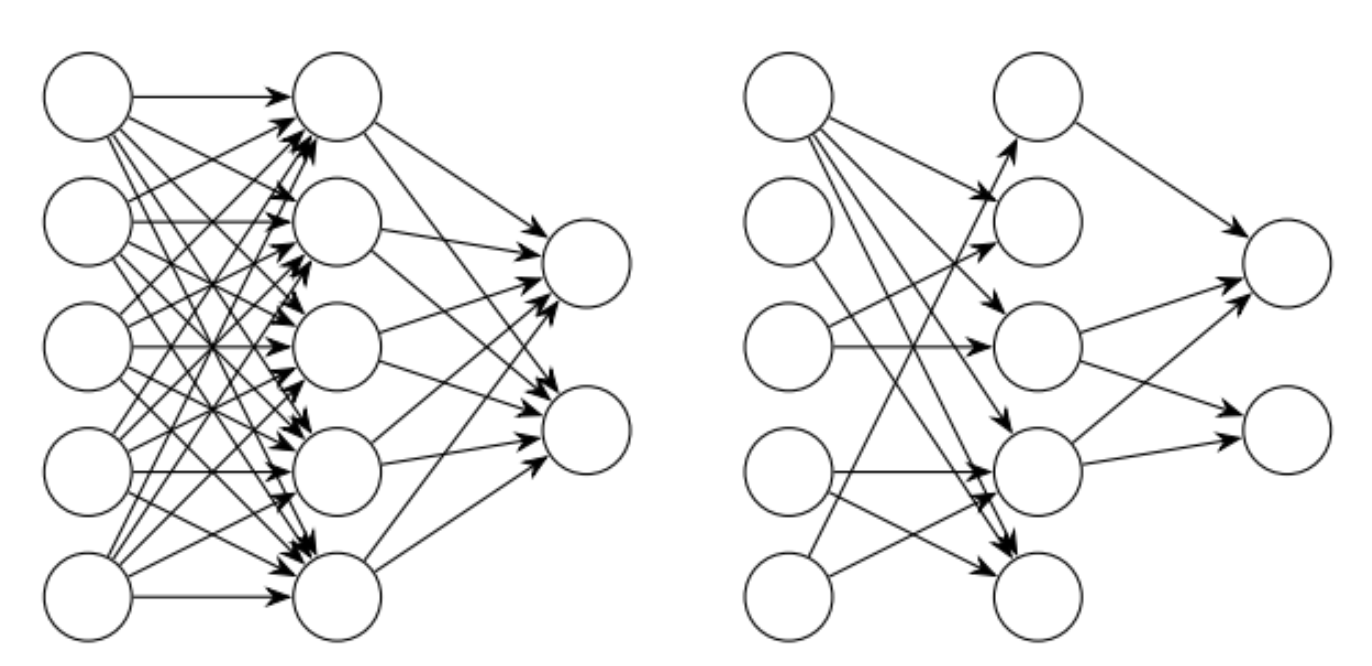
drop connect:
- 不是随机的将隐层节点的输出变成0,而是将节点中的每个与其相连的输入权值以1-p的概率变成0。(一个是输出一个是输入)
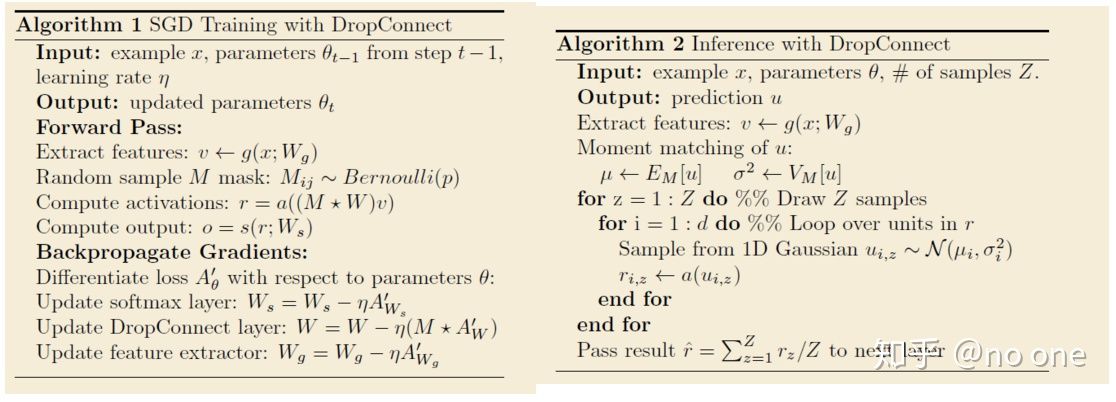
- 训练阶段,对每个example/mini-batch, 每个epoch都随机sample一个mask矩阵
Dropconnect在测试期间采用了与标准dropout不同的方法。作者提出了dropconnect在每个神经元处的高斯近似,然后从这个高斯函数中抽取一个样本并传递给神经元激活函数。这使得dropconnect在测试时和训练时都是一种随机方法。
伯努利分布:0-1分布
dropout & drop connect 通常只作用于全连接层上:这俩是用来防止过多参数导致过拟合
卷积层参数贼少,所以没必要,
针对卷积通道有spacial dropout:按照channel随机扔
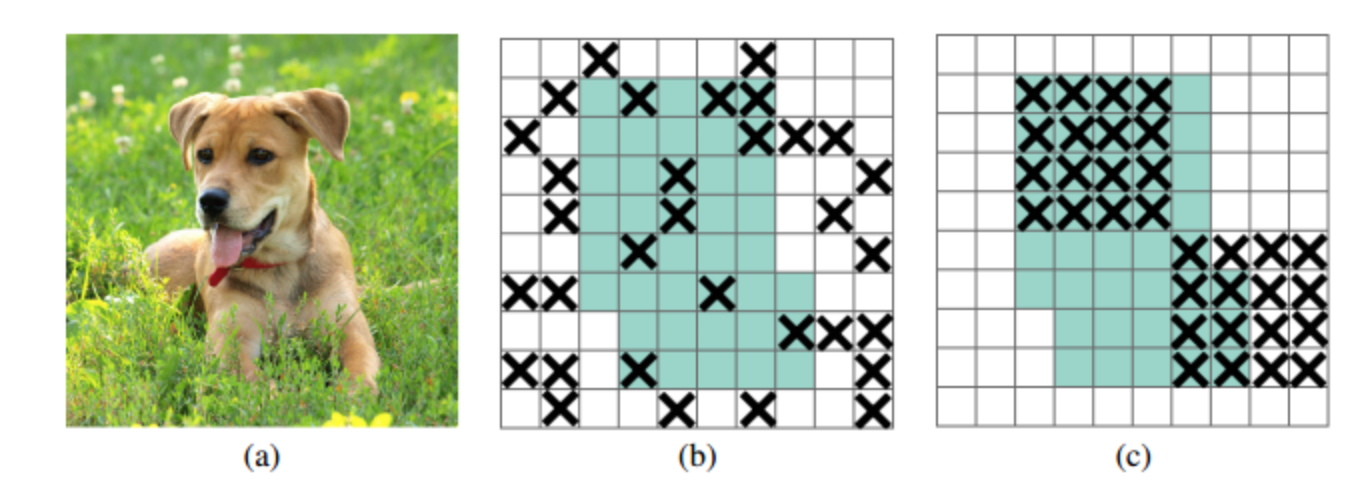
dropblock:是针对卷积层的正则化方法,相比较于dropout的random mute,能够更有效地remove掉部分语义信息,block size=1的时候退化成dropout
papers
[dropout] Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors,丢节点
[drop connect] Regularization of neural networks using dropconnect,丢weight path
[Stochastic Depth] Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth,丢layer
[DropBlock] A regularization method for convolutional networks
drop大法一句话汇总
- dropout:各维度完全随机扔
- spacial dropout:按照channel随机扔
- stochastic depth:按照res block随机扔
- dropblock:在feature map上按照spacial块随机扔
- cutout:在input map上按照spacial块随机扔
- dropconnect:扔连接不扔神经元
Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth
动机
- propose a training procedure:stochastic depth,train short and test deep
- for each mini-batch
- randomly drop a subset of layers
- and bypass them with the identity function
- short:reduces training time
- reg:improves the test error
- can increase the network depth
论点
deeper
- expressiveness
- vanishing gradients
- diminishing feature reuse
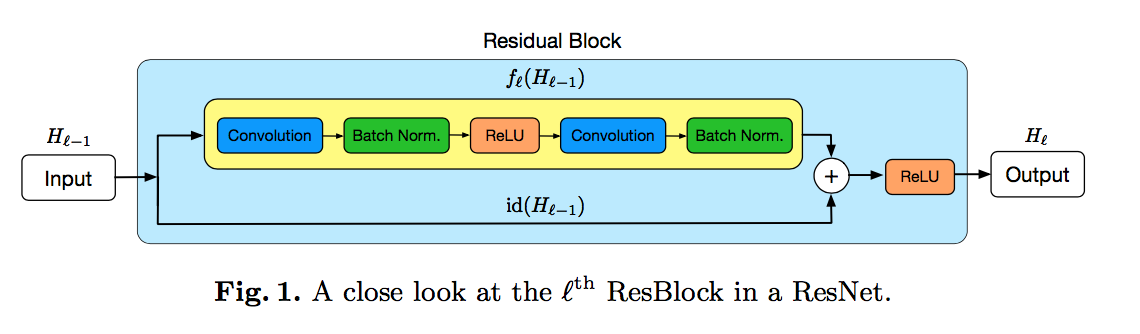
resnet
- skip connection
when输入输出channel数不match:redefine id(·) as a linear projection to reduce the dimensions
dropout
- Dropout reduces the effect known as “co- adaptation” of hidden nodes
- Dropout loses effectiveness when used in combination with Batch Normalization
our approach
- higher diversity
- shorter instead of thinner
- work with Batch Normalization
方法
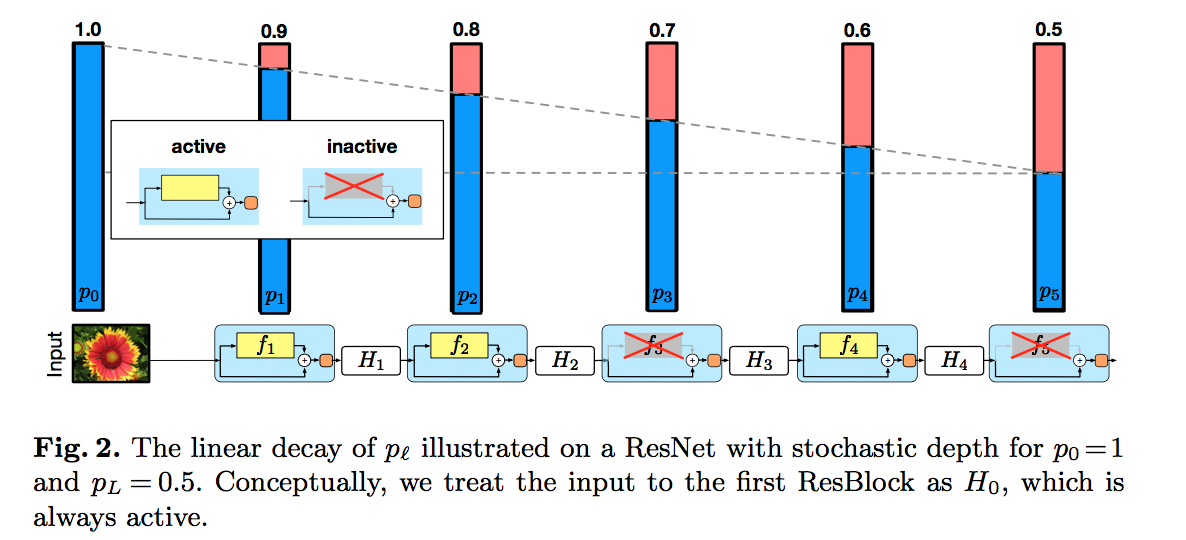
stochastic depth
- randomly dropping entire ResBlocks
- $H_l = ReLU(b_l Res_l(H_{l-1}) + id(H_{l-1}))$
survival probabilities
$p_l = Pr(b_l=1)$
set uniformly / set following a linear decay rule
set $p_0=1, p_L=0.5$:
intuition:the earlier layers extract low-level features that will be used by later layers and should therefore be more reliably present
Expected network depth
- $E(L) \approx 3L/4$
- approximately 25% of training time could be saved
during testing
- all res path are active
- each res path is weighted by its survival probability
- $H_l^{Test} = ReLU(b_l Res_l(H_{l-1}, W_l) + id(H_{l-1}))$
- 跟dropout一样