challenge
Large Scale Vertebrae Segmentation Challenge
- task1:Vertebra Labelling,关键点检测
- task2:Vertebra Segmentation,多类别分割
data

- variation:数据affine轴不统一,尺寸不统一,扫描范围不统一,FOV区域不统一
- nii的两大解析工具:nibabel库load data的xyz顺序与axcode的顺序一致,e.g.[‘R’,’A’,’S’]的orientation会得到xyz的array,而sitk的读取刚好反过来,sitk的arr会是zyx。我们之前在将dicom写入nii时,会指定一个不为np.eye(4)的affine,就是为了transpose这三个轴。
model
team paper \
三阶段:第一阶段,due to large variation FOV of the dataset,粗分割定位脊柱位置,第二阶段,higher resolution多类别关键点定位center,获得each located vertebra,第三阶段,二类分割for each located vertebra。
keywords:1. uniform voxel spacing:不要随意resize,todo: trilinear interp;2. on-the-fly data augmentation:using SimpleITK
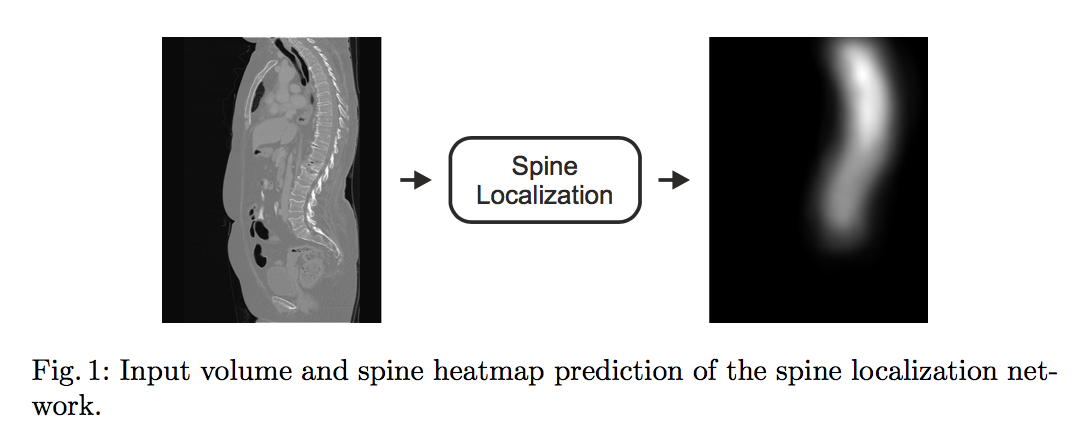
第一阶段:Spine Localization
- Unet
- regress the Gaussian heatmap of spinal centerline
- L2-loss
- uniform voxel spacing of 8mm
input shape:[64,64,128],pad?
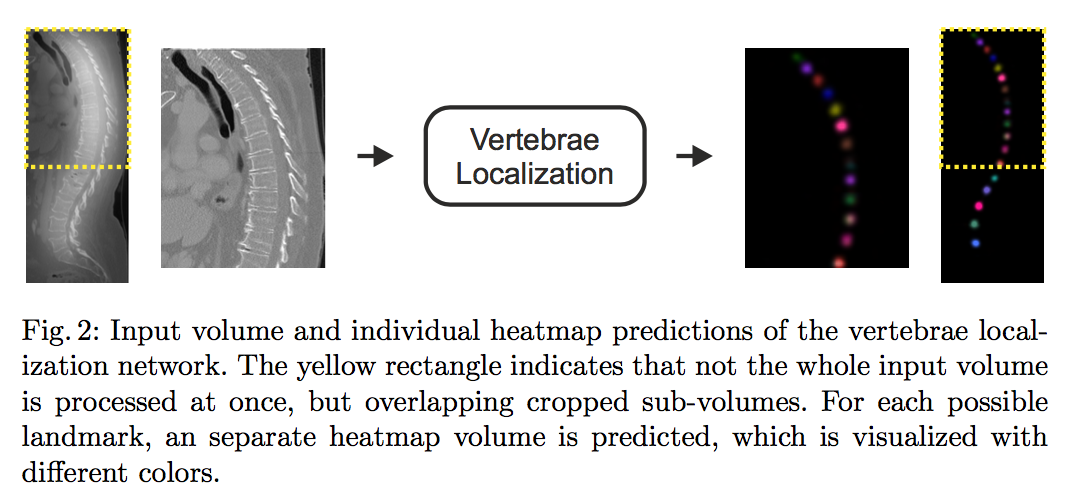
第二阶段:Vertebrae Localization
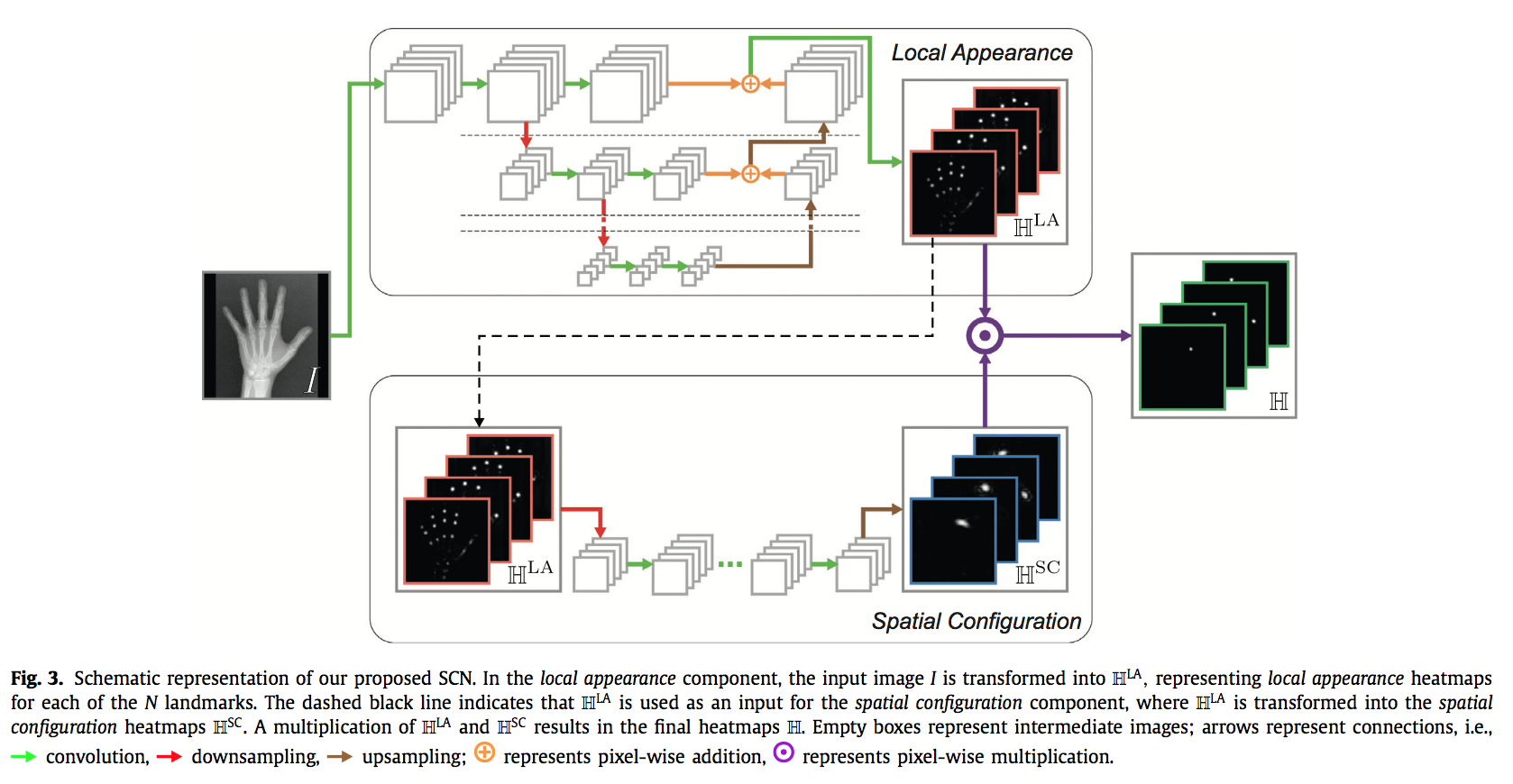
- SpatialConfiguration-Net
- regress each located vertebra‘s heatmap in individual channel
- resampling:bi/tricubic interpolation
- norm:maxmin on the whole dataset
- uniform voxel spacing of 2mm
input shape:[96,96,128],z-axis random crop,xy-plane use ROI from stage1
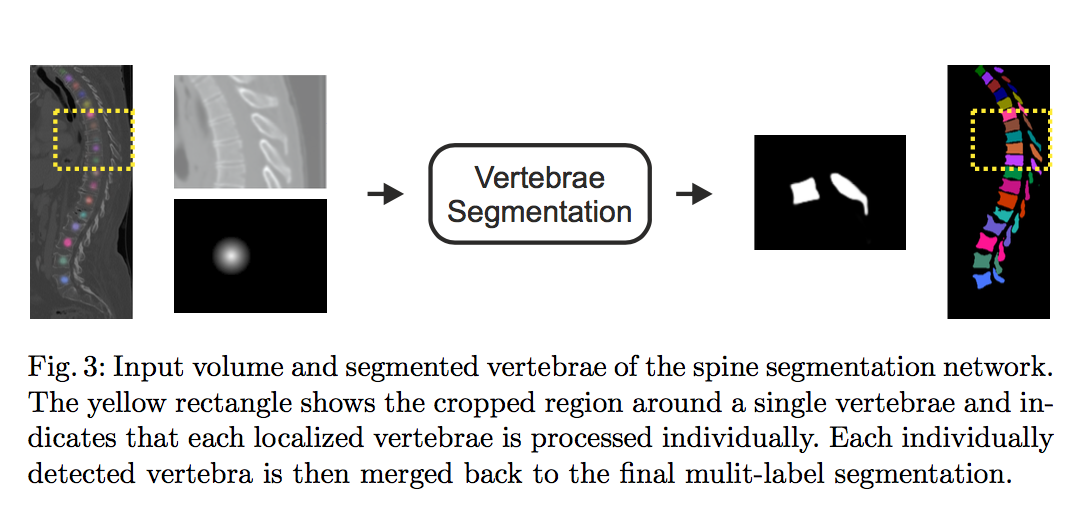
第三阶段:Vertebrae Segmentation
- Unet
- binary segment the mask of each vertebrae
- sigmoid ce-loss
- uniform voxel spacing of 1mm
input shape:[128,128,96],crop origin image & heatmap image based on centroids
reference paper\
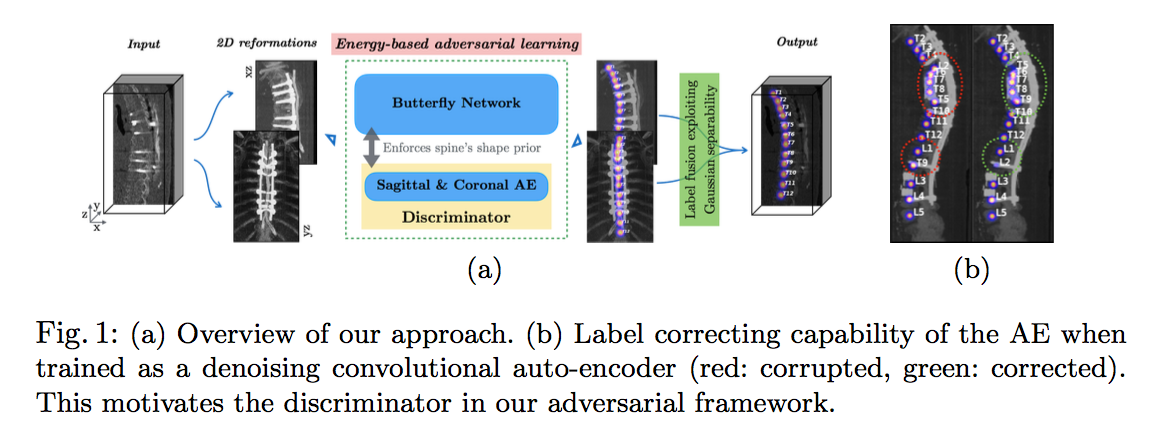
- 核心贡献:1.MIP:combines the information across reformations,3D to 2D,2. 基于判别器的训练机制:encodes local spine structure as an anatomical prior,加固椎块间类别&位置的spacial information
- MIP:
- localisation and identification rely on a large context
- large receptive field
- in full-body scans where spine is not spatially centred or is obstructed by the ribcage, such cases are handled with a pre-processing stage detecting the occluded spine
adversarial learning:
- FCN用于分割
- AE用于评估分割的好坏
- do not ‘pre-train’ it (the AE)
- loss:an anatomically-inspired supervision instead of the usual binary adversarial supervision (vanilla GAN)
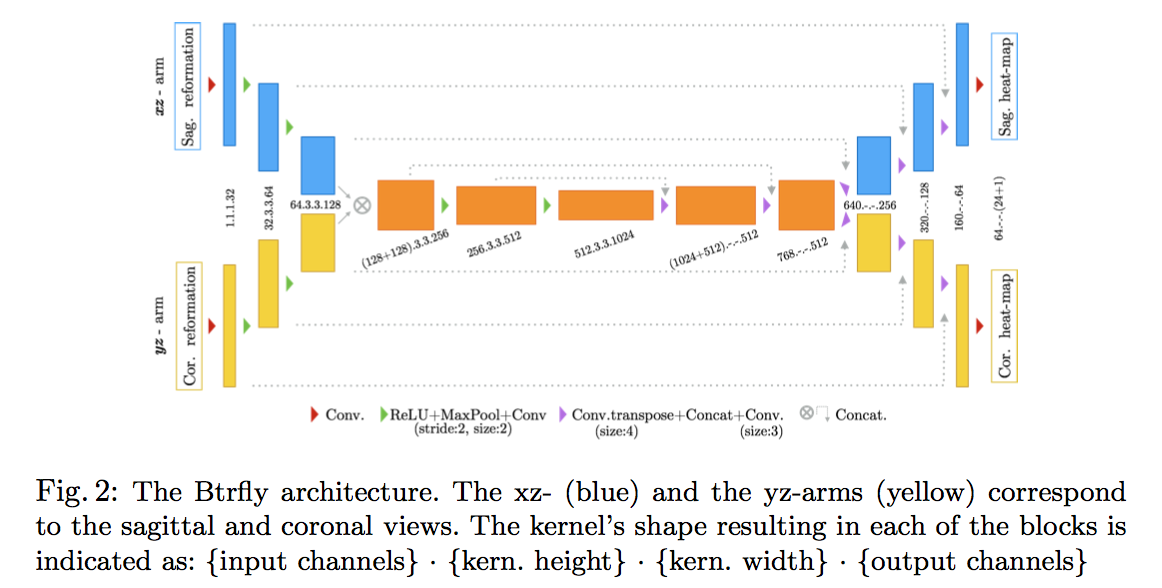
先说FCN——Btrfly Network
建模成回归问题,每个关键点对应一个通道的高斯heatmap,背景channel为$1-max_i (y_i)$
双输入双输出(sagittal & coronal)
两个视角的feature map在网络深层做了融合,to learn their inter-dependency
Batch- normalisation is used after every convolution layer, along with 20% dropout in the fused layers of Btrfly
loss:l2 distance + weighted ce
$\omega$ is the median frequency weighing map, boosting the learning of less frequent classes(ECB)
再说判别器——Energy-based adversary for encoding prior
fully-convolutional:its predictions across voxels are independent of each other owing to the spatial invariance of convolutions
to impose the anatomical prior of the spine’s shape onto the Btrfly net
look at $\hat{Y}_{sag}$ and $\hat{Y}_{cor}$ as a 3D volume and employ a 3D AE with a receptive field covering a part of the spine
$\hat{Y}_{sag}$ consists of Gaussians:less informative than an image, avoid using max-pooling by resorting to average pooling
employ spatially dilated convolution kernels
mission of AE:predict the l2 distance of input and its reconstruction, it learns to discriminate by predicting a low E for real annotations, while G learns to generate annotations that would trick D

inference:
- The values below a threshold (T) are ignored in order to remove noisy predictions
- 用外积,$\hat{Y}=\hat{Y}_{sag}\otimes\hat{Y}_{cor}$
- 每个channel的最大值作为centroids
experiments
- 【IMPORTANT】10 MIPs are obtained from one 3D scan per view, each time randomly choosing half the slices of interest
- 对于每个视角,每次随机抽取一半数目的slice用于计算MIP
similar local appearance:
strong spatial configuration:凡是涉及到椎块-wise的信息,从全局信息入手