基于极其标准的图优化SLAM框架来实现:
提出了采用稀疏点调整(SPA)的方法来高效求解位姿图优化问题,针对本算法的文献为《Efficient Sparse Pose Adjustment for 2D Mapping》。
scan matching部分的参考文献为《Real-time correlative scan matching》,M3RSM的前身!
key concepts:
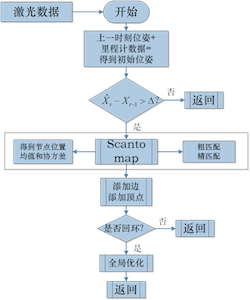
keyScan:机器人运动一定的距离或角度(关键帧),储存在sensorManager,无地图缓存。
look-up table查找表:查找表的意义就是相比于暴力匹配,不需要每次都重新计算每个激光数据信息,相同角度不同位置的激光数据信息只需要被索引一次。
response响应值:将查找表以一定的位移投到子图上,总共有n个点被查找表击中(hit),击中的每个点得分不同(score),累加得分并除以可以达到的最高分。
协方差:文献专门用了一节计算协方差,但是没看到用在哪,是为了后面求误差做准备吗???
addScans添加顶点和边:边是误差值,添加的边约束来自两部分,
(1)link to running scans,距当前帧一定范围内的激光数据链(RunningScan chain)。
(2)link to other near chains,从当前节点开始广度优先遍历一定距离范围内所有节点,依据当前id从sensorManager中分别递增和递减寻找一定范围内的chain(不一定直接相连)。
回环检测:操作与添加边约束类似,位姿图上要去除那些和当前节点的时间相邻的节点。
(1)找到一定距离范围内(near)和相连(adjacent)的节点添加进nearLinkedScans。
(2)
MapperGraph::FindPossibleLoopClosure:从sensorManager中从前到后,依据序号挑选与当前节点在一定距离范围内,且不在nearLinkedScans中的candidate。返回潜在chain。其中涉及两个参数:- LoopSearchMaximumDistance:candidateScan与当前scan的距离必须在可容许的距离内。
- LoopMatchMinimumChainSize:chain中的节点数必须不小于限定值。
(3)
MapperGraph::TryCloseLoop:scan2map匹配,当response和covariance达到一定要求认为闭环检测到,得到correct pose(也就是认为candidateScan的pose才是当前帧的实际pose)。(4)add link to loop,构成全局闭环。
(5)触发correctPose,进行spa优化。
代码随手记:
ROS上面提供三个开源包:nav2d_karto, open_karto, slam_karto。
ROS Wiki上这么描述nav2d_karto这个package:Graph-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping module. Includes OpenKarto GraphSLAM library by “SRI International”.
open_karto:开源的karto包,实现底层的kartoslam
slam_karto:ros层,应用层的kartoslam接口
The LaserRangeFinder contains parameters for physical laser sensor used by the mapper for scan matching Also contains information about the maximum range of the sensor and provides a threshold for limiting the range of readings.
The optimal value for the range threshold depends on the angular resolution of the scan and the desired map resolution.
resolution:0.25 & 0.5 & 1 degree
number of range readings (beams):(maximumAngle - minimumAngle)/angularResolution + 1
GridStates:0 for Unknown,100 for Occupied, 255 for Free。
flipY:最开始机器人应该处在世界坐标系的原点,传感器坐标系与机器人baselink存在一个坐标变换,原始的传感器坐标系位置应该与地图坐标系重合,这就是world和grid之间的offset。flip是啥呢??
LookupArray[index]:Create lookup tables for point readings at varying angles in grid. This is to speed up finding best angle/position for a localized range scan
MapperGraph:花式构造位姿图
CorrelationGrid:Implementation of a correlation grid used for scan matching
Region of Interest ROI:
smear:The point readings are smeared by this value in X and Y to create a smoother response. 个人理解这句话是说点容易生成突变,用以点为中心的一小片区域平滑一点。
ScanMatch:返回响应值response
前端匹配调用
m_pSequentialScanMatcher->MatchScan闭环检测调用
m_pLoopScanMatcher->MatchScan两个函数继承于
ScanMatcher::MatchScan:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8kt_double ScanMatcher::MatchScan(
LocalizedRangeScan* pScan,
const LocalizedRangeScanVector& rBaseScans,
Pose2& rMean,
Matrix3& rCovariance,
kt_bool doPenalize,
kt_bool doRefineMatch) // default is True, 决定是否做精匹配
// @return: strength of response (best response)其中会调用
ScanMatcher::CorrelateScan方法。ScanMatcher::CorrelateScan方法中调用ScanMatcher::GetResponse方法计算响应值。1
2
3kt_double ScanMatcher::GetResponse(
kt_int32u angleIndex,
kt_int32s gridPositionIndex) constGetResponse的核心在kt_int8u* pByte和const LookupArray* pOffsets两个数据结构:- 前者是在correlationGrid范围内的real sensed占据情况。
后者是lookup-table中(已知地图)读取的栅格占据情况,只包含占据的栅格,key是angular。
计算response只要看地图上的占据点是否在观测中是否也是占据的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12for (kt_int32u i = 0; i < pOffsets->GetSize(); i++)
{
// ignore points that fall off the grid
kt_int32s pointGridIndex = gridPositionIndex + pAngleIndexPointer[i];
if (!math::IsUpTo(pointGridIndex, m_pCorrelationGrid->GetDataSize()) || pAngleIndexPointer[i] == INVALID_SCAN)
{
continue;
}
// uses index offsets to efficiently find location of point in the grid
response += pByte[pAngleIndexPointer[i]];
}最终的response要normalize:
1
2
3// normalize response
response /= (nPoints * GridStates_Occupied); // GridStates_Occupied = 100,
assert(fabs(response) <= 1.0);
karto只在闭环的时候触发后端优化
CorrectPoses(),ScanSolver的实现在Samples路径下的SpaSolver,调用了现有的BA求解器sba(A Generic Sparse Bundle Adjustment C/C++ Package Based on the Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm)。
参数&优化方向
- 闭环中candidate数量的调整:
- 减小LoopSearchMaximumDistance,进入candidate范围的节点数据减少
- 减小LoopMatchMinimumChainSize,用来计算优化的candidate数量减少
- 增大minimum_travel_distance和minimum_travel_heading,这样总体的节点数减少
- Map_update_interval:发布地图的间隔,其主要过程是遍历当前所有节点数据,对每个栅格的占有状态进行判定,生成栅格地图。
- ScanBufferSize和ScanBufferMaximumScanDistance:控制buffer也就是chain的大小。chain不能太大也不能太小,太小会造成前端误差累积,太大会导致构建闭环的节点数不足。推荐值是ScanBufferMaximumScanDistance/minimum_travel_distance。
- 位姿纠正中:
- CorrelationSearchSpaceDimension:The size of the search grid
- CorrelationSearchSpaceResolution:The size of the correlation grid
- 回环检测中:
- LoopSearchMaximumDistance:闭环检测的搜索距离,数值越大能越早发现闭环,也能容忍更大的偏离误差。
- LoopMatchMinimumResponseCoarse和LoopMatchMinimumResponseFine:粗匹配和精匹配的响应阈值,与闭环中candidate数量相关。阈值过低会导致candidate迅速被填满,真正好的点还没找到。阈值过高会导致回环失败(一直找不到回环点),地图上出现重影。
CPU Usage
算法资源占用的主要压力来源:
- 地图更新
- 回环检测
- SPA优化